
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in construction facilitates the creation of detailed digital designs in both 2D and 3D. This technology allows teams to design, modify, and simulate projects accurately, optimising resources and time. Additionally, it reduces costs by anticipating errors and improves communication between stakeholders, ensuring the correct execution of each stage of the construction process.
In traditional surveying, CAD complements the information collected by surveyors by developing detailed two-dimensional plans. In LiDAR laser scanning, CAD enables the handling of three-dimensional models generated from point clouds, facilitating their analysis and use in design.
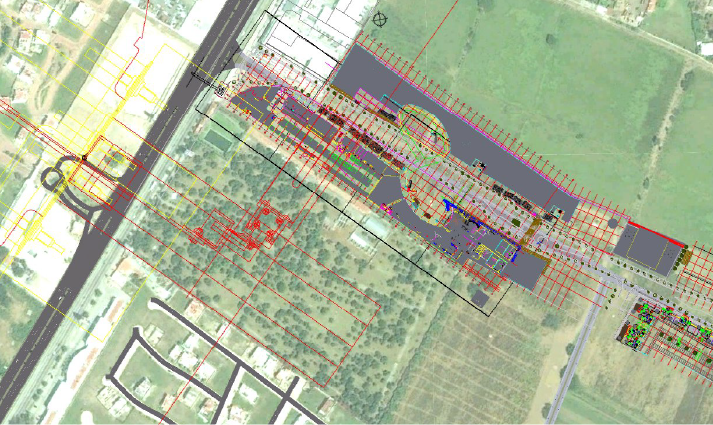
CAD platforms enable teams to share and modify designs in real time. This fosters smooth communication between architects, engineers, and contractors, ensuring everyone is aligned with the project in progress.
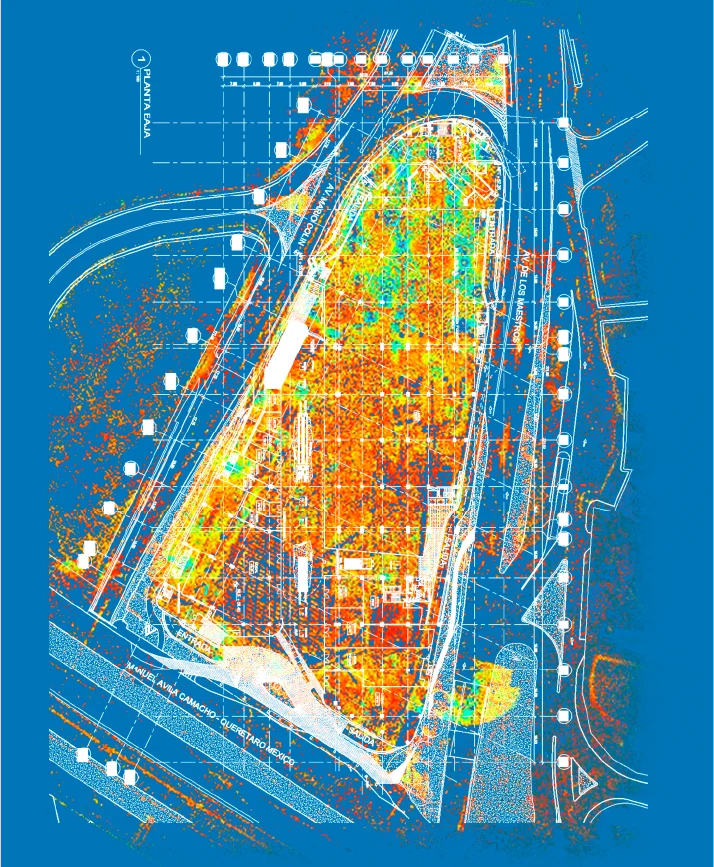
CAD provides 3D models that deliver an accurate visual representation of projects. This allows all stakeholders to better understand the final design, facilitating decision-making and identifying problems before construction begins.

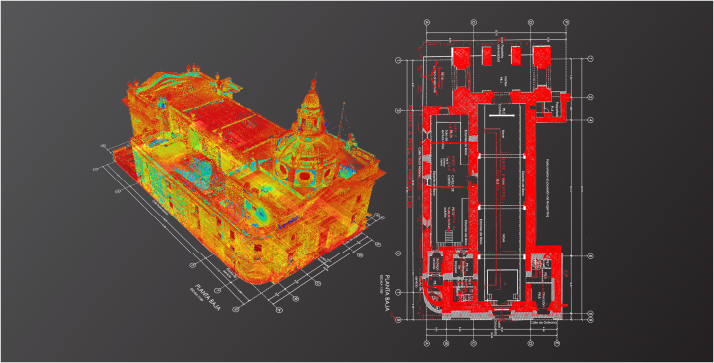
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in construction facilitates the creation of detailed digital designs in both 2D and 3D. This technology allows teams to design, modify, and simulate projects accurately, optimising resources and time. Additionally, it reduces costs by anticipating errors and improves communication between stakeholders, ensuring the correct execution of each stage of the construction process.
In traditional surveying, CAD complements the information collected by surveyors by developing detailed two-dimensional plans. In LiDAR laser scanning, CAD enables the handling of three-dimensional models generated from point clouds, facilitating their analysis and use in design.
CAD platforms enable teams to share and modify designs in real time. This fosters smooth communication between architects, engineers, and contractors, ensuring everyone is aligned with the project in progress.
CAD provides 3D models that deliver an accurate visual representation of projects. This allows all stakeholders to better understand the final design, facilitating decision-making and identifying problems before construction begins.